| Copyright | Clemens Fruhwirth <clemens@endorphin.org> |
|---|---|
| License | BSD-style (see LICENSE) |
| Maintainer | Clemens Fruhwirth <clemens@endorphin.org> |
| Stability | unstable |
| Portability | unportable |
| Safe Haskell | Safe-Inferred |
| Language | Haskell2010 |
XMonad.Actions.GridSelect
Description
GridSelect displays items(e.g. the opened windows) in a 2D grid and lets the user select from it with the cursor/hjkl keys or the mouse.
Synopsis
- data GSConfig a = GSConfig {
- gs_cellheight :: Integer
- gs_cellwidth :: Integer
- gs_cellpadding :: Integer
- gs_colorizer :: a -> Bool -> X (String, String)
- gs_font :: String
- gs_navigate :: TwoD a (Maybe a)
- gs_rearranger :: Rearranger a
- gs_originFractX :: Double
- gs_originFractY :: Double
- gs_bordercolor :: String
- gs_cancelOnEmptyClick :: Bool
- def :: Default a => a
- type TwoDPosition = (Integer, Integer)
- buildDefaultGSConfig :: (a -> Bool -> X (String, String)) -> GSConfig a
- gridselect :: GSConfig a -> [(String, a)] -> X (Maybe a)
- gridselectWindow :: GSConfig Window -> X (Maybe Window)
- withSelectedWindow :: (Window -> X ()) -> GSConfig Window -> X ()
- bringSelected :: GSConfig Window -> X ()
- goToSelected :: GSConfig Window -> X ()
- gridselectWorkspace :: GSConfig WorkspaceId -> (WorkspaceId -> WindowSet -> WindowSet) -> X ()
- gridselectWorkspace' :: GSConfig WorkspaceId -> (WorkspaceId -> X ()) -> X ()
- spawnSelected :: GSConfig String -> [String] -> X ()
- runSelectedAction :: GSConfig (X ()) -> [(String, X ())] -> X ()
- class HasColorizer a where
- defaultColorizer :: a -> Bool -> X (String, String)
- fromClassName :: Window -> Bool -> X (String, String)
- stringColorizer :: String -> Bool -> X (String, String)
- colorRangeFromClassName :: (Word8, Word8, Word8) -> (Word8, Word8, Word8) -> (Word8, Word8, Word8) -> (Word8, Word8, Word8) -> (Word8, Word8, Word8) -> Window -> Bool -> X (String, String)
- stringToRatio :: String -> Double
- data TwoD a b
- makeXEventhandler :: ((KeySym, String, KeyMask) -> TwoD a (Maybe a)) -> TwoD a (Maybe a)
- shadowWithKeymap :: Map (KeyMask, KeySym) a -> ((KeySym, String, KeyMask) -> a) -> (KeySym, String, KeyMask) -> a
- defaultNavigation :: TwoD a (Maybe a)
- substringSearch :: TwoD a (Maybe a) -> TwoD a (Maybe a)
- navNSearch :: TwoD a (Maybe a)
- setPos :: (Integer, Integer) -> TwoD a ()
- move :: (Integer, Integer) -> TwoD a ()
- moveNext :: TwoD a ()
- movePrev :: TwoD a ()
- select :: TwoD a (Maybe a)
- cancel :: TwoD a (Maybe a)
- transformSearchString :: (String -> String) -> TwoD a ()
- type Rearranger a = String -> [(String, a)] -> X [(String, a)]
- noRearranger :: Rearranger a
- searchStringRearrangerGenerator :: (String -> a) -> Rearranger a
- data TwoDState a
Usage
You can use this module with the following in your xmonad.hs:
import XMonad.Actions.GridSelect
Then add a keybinding, e.g.
, ((modm, xK_g), goToSelected def)
This module also supports displaying arbitrary information in a grid and letting the user select from it. E.g. to spawn an application from a given list, you can use the following:
, ((modm, xK_s), spawnSelected def ["xterm","gmplayer","gvim"])
Customizing
Using a common GSConfig
It is possible to bind a gsconfig at top-level in your configuration. Like so:
-- the top of your config
{-# LANGUAGE NoMonomorphismRestriction #-}
import XMonad
...
gsconfig1 = def { gs_cellheight = 30, gs_cellwidth = 100 }An example where buildDefaultGSConfig is used instead of def
in order to specify a custom colorizer is gsconfig2 (found in
XMonad.Actions.GridSelect):
gsconfig2 colorizer = (buildDefaultGSConfig colorizer) { gs_cellheight = 30, gs_cellwidth = 100 }-- | A green monochrome colorizer based on window class
greenColorizer = colorRangeFromClassName
black -- lowest inactive bg
(0x70,0xFF,0x70) -- highest inactive bg
black -- active bg
white -- inactive fg
white -- active fg
where black = minBound
white = maxBoundThen you can bind to:
,((modm, xK_g), goToSelected $ gsconfig2 myWinColorizer)
,((modm, xK_p), spawnSelected (gsconfig2 defaultColorizer) ["xterm","gvim"])Custom keybindings
You can build you own navigation mode and submodes by combining the
exported action ingredients and assembling them using makeXEventhandler and shadowWithKeymap.
myNavigation :: TwoD a (Maybe a)
myNavigation = makeXEventhandler $ shadowWithKeymap navKeyMap navDefaultHandler
where navKeyMap = M.fromList [
((0,xK_Escape), cancel)
,((0,xK_Return), select)
,((0,xK_slash) , substringSearch myNavigation)
,((0,xK_Left) , move (-1,0) >> myNavigation)
,((0,xK_h) , move (-1,0) >> myNavigation)
,((0,xK_Right) , move (1,0) >> myNavigation)
,((0,xK_l) , move (1,0) >> myNavigation)
,((0,xK_Down) , move (0,1) >> myNavigation)
,((0,xK_j) , move (0,1) >> myNavigation)
,((0,xK_Up) , move (0,-1) >> myNavigation)
,((0,xK_y) , move (-1,-1) >> myNavigation)
,((0,xK_i) , move (1,-1) >> myNavigation)
,((0,xK_n) , move (-1,1) >> myNavigation)
,((0,xK_m) , move (1,-1) >> myNavigation)
,((0,xK_space) , setPos (0,0) >> myNavigation)
]
-- The navigation handler ignores unknown key symbols
navDefaultHandler = const myNavigationYou can then define gsconfig3 which may be used in exactly the same manner as gsconfig1:
gsconfig3 = def
{ gs_cellheight = 30
, gs_cellwidth = 100
, gs_navigate = myNavigation
}Configuration
The Default instance gives a basic configuration for gridselect, with
the colorizer chosen based on the type.
If you want to replace the gs_colorizer field, use buildDefaultGSConfig
instead of def to avoid ambiguous type variables.
Constructors
| GSConfig | |
Fields
| |
Instances
| HasColorizer a => Default (GSConfig a) Source # | |
Defined in XMonad.Actions.GridSelect | |
type TwoDPosition = (Integer, Integer) Source #
buildDefaultGSConfig :: (a -> Bool -> X (String, String)) -> GSConfig a Source #
Builds a default gs config from a colorizer function.
Variations on gridselect
gridselect :: GSConfig a -> [(String, a)] -> X (Maybe a) Source #
Brings up a 2D grid of elements in the center of the screen, and one can select an element with cursors keys. The selected element is returned.
gridselectWindow :: GSConfig Window -> X (Maybe Window) Source #
Like gridSelect but with the current windows and their titles as elements
withSelectedWindow :: (Window -> X ()) -> GSConfig Window -> X () Source #
Brings up a 2D grid of windows in the center of the screen, and one can select a window with cursors keys. The selected window is then passed to a callback function.
goToSelected :: GSConfig Window -> X () Source #
Switches to selected window's workspace and focuses that window.
gridselectWorkspace :: GSConfig WorkspaceId -> (WorkspaceId -> WindowSet -> WindowSet) -> X () Source #
Select a workspace and view it using the given function
(normally view or greedyView)
Another option is to shift the current window to the selected workspace:
gridselectWorkspace (\ws -> W.greedyView ws . W.shift ws)
gridselectWorkspace' :: GSConfig WorkspaceId -> (WorkspaceId -> X ()) -> X () Source #
Select a workspace and run an arbitrary action on it.
spawnSelected :: GSConfig String -> [String] -> X () Source #
Select an application to spawn from a given list
runSelectedAction :: GSConfig (X ()) -> [(String, X ())] -> X () Source #
Select an action and run it in the X monad
Colorizers
class HasColorizer a where Source #
That is fromClassName if you are selecting a Window, or
defaultColorizer if you are selecting a String. The catch-all instance
HasColorizer a uses the focusedBorderColor and normalBorderColor
colors.
Instances
| HasColorizer Window Source # | |
Defined in XMonad.Actions.GridSelect | |
| HasColorizer String Source # | |
Defined in XMonad.Actions.GridSelect | |
| HasColorizer a Source # | |
Defined in XMonad.Actions.GridSelect | |
fromClassName :: Window -> Bool -> X (String, String) Source #
Colorize a window depending on it's className.
colorRangeFromClassName Source #
Arguments
| :: (Word8, Word8, Word8) | Beginning of the color range |
| -> (Word8, Word8, Word8) | End of the color range |
| -> (Word8, Word8, Word8) | Background of the active window |
| -> (Word8, Word8, Word8) | Inactive text color |
| -> (Word8, Word8, Word8) | Active text color |
| -> Window | |
| -> Bool | |
| -> X (String, String) |
A colorizer that picks a color inside a range, and depending on the window's class.
stringToRatio :: String -> Double Source #
Generates a Double from a string, trying to achieve a random distribution. We create a random seed from the hash of all characters in the string, and use it to generate a ratio between 0 and 1
Navigation Mode assembly
makeXEventhandler :: ((KeySym, String, KeyMask) -> TwoD a (Maybe a)) -> TwoD a (Maybe a) Source #
Embeds a key handler into the X event handler that dispatches key events to the key handler, while non-key event go to the standard handler.
shadowWithKeymap :: Map (KeyMask, KeySym) a -> ((KeySym, String, KeyMask) -> a) -> (KeySym, String, KeyMask) -> a Source #
When the map contains (KeySym,KeyMask) tuple for the given event, the associated action in the map associated shadows the default key handler
Built-in Navigation Mode
defaultNavigation :: TwoD a (Maybe a) Source #
By default gridselect used the defaultNavigation action, which
binds left,right,up,down and vi-style h,l,j,k navigation. Return
quits gridselect, returning the selected element, while Escape
cancels the selection. Slash enters the substring search mode. In
substring search mode, every string-associated keystroke is
added to a search string, which narrows down the object
selection. Substring search mode comes back to regular navigation
via Return, while Escape cancels the search. If you want that
navigation style, add defaultNavigation as gs_navigate to your
GSConfig object. This is done by buildDefaultGSConfig automatically.
substringSearch :: TwoD a (Maybe a) -> TwoD a (Maybe a) Source #
Navigation submode used for substring search. It returns to the first argument navigation style when the user hits Return.
navNSearch :: TwoD a (Maybe a) Source #
This navigation style combines navigation and search into one mode at the cost of losing vi style navigation. With this style, there is no substring search submode, but every typed character is added to the substring search.
Navigation Components
transformSearchString :: (String -> String) -> TwoD a () Source #
Apply a transformation function the current search string
Rearrangers
Rearrangers allow for arbitrary post-filter rearranging of the grid elements.
For example, to be able to switch to a new dynamic workspace by typing in its name, you can use the following keybinding action:
import XMonad.Actions.DynamicWorkspaces (addWorkspace)
gridselectWorkspace' def
{ gs_navigate = navNSearch
, gs_rearranger = searchStringRearrangerGenerator id
}
addWorkspacetype Rearranger a = String -> [(String, a)] -> X [(String, a)] Source #
A function taking the search string and a list of elements, and returning a potentially rearranged list of elements.
noRearranger :: Rearranger a Source #
A rearranger that leaves the elements unmodified.
searchStringRearrangerGenerator :: (String -> a) -> Rearranger a Source #
A generator for rearrangers that append a single element based on the search string, if doing so would not be redundant (empty string or value already present).
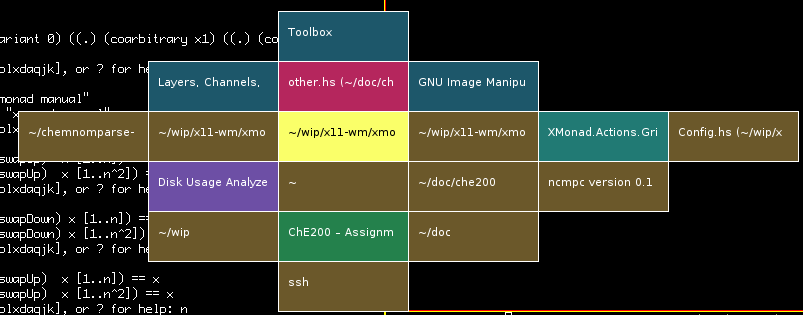
Screenshots
Selecting a workspace:

Selecting a window by title: